SpringBean生命周期
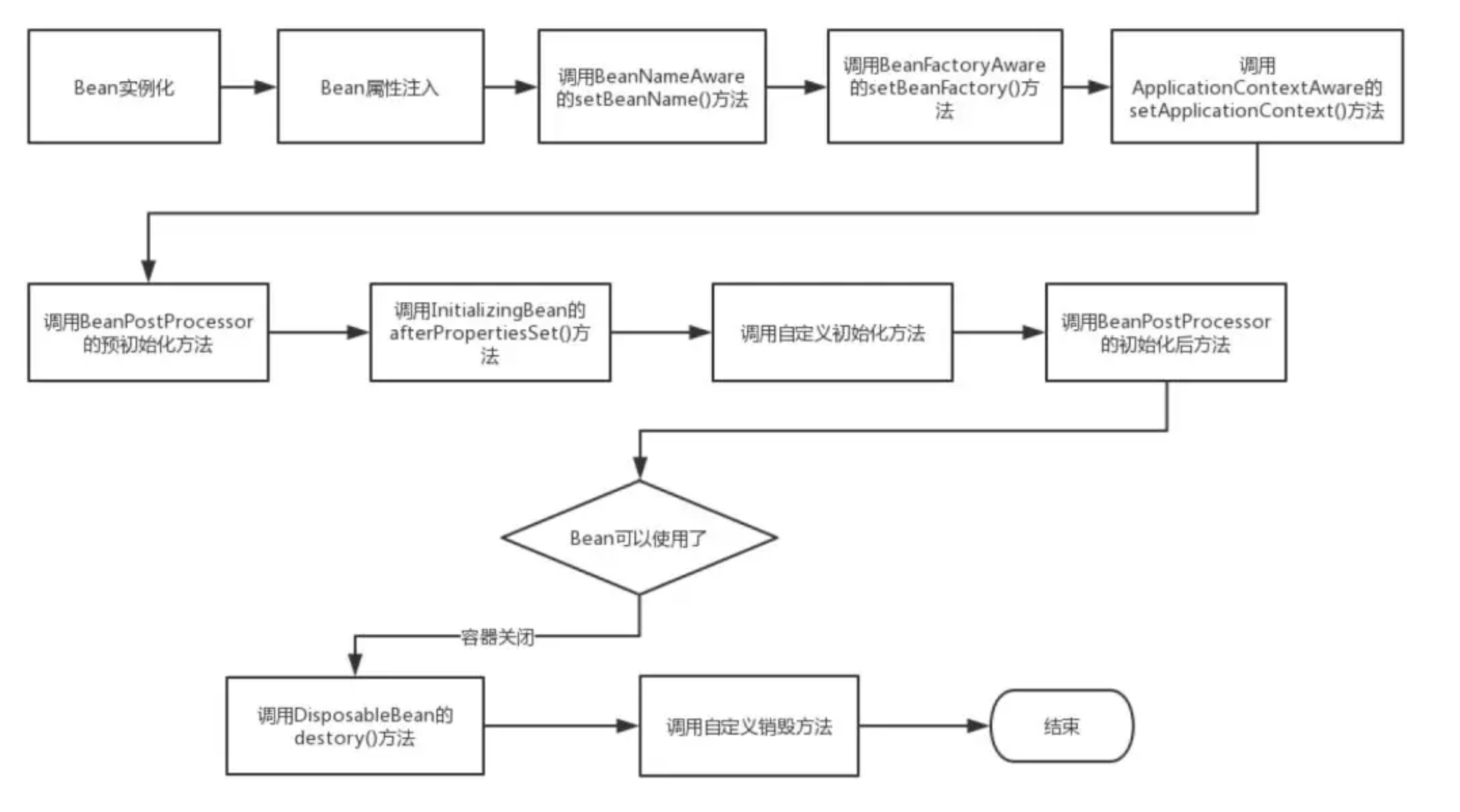
Bean生命周期
- Spring启动,查找并加载需要被Spring管理的bean,进行Bean的实例化
- Bean实例化后对将Bean的引入和值注入到Bean的属性中
- 如果Bean实现了
BeanNameAware接口的话,Spring将Bean的Id传递给setBeanName()方法 - 如果Bean实现了
BeanFactoryAware接口的话,Spring将调用setBeanFactory()方法,将BeanFactory容器实例传入 - 如果Bean实现了
ApplicationContextAware接口的话,Spring将调用Bean的setApplicationContext()方法,将bean所在应用上下文引用传入进来 - 如果Bean实现了
BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring就将调用他们的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法 - 如果Bean实现了
InitializingBean接口,Spring将调用他们的afterPropertiesSet()方法。类似的,如果bean使用init-method声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用 - 如果Bean实现了
BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring就将调用他们的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法 - 此时,Bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁
- 如果bean实现了
DisposableBean接口,Spring将调用它的destory()接口方法,同样,如果bean使用了destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用
验证Bean生命周期
public class Book implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String bookName;
public Book(){
System.out.println("Book Initializing");
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("Book.setBeanFactory invoke");
}
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("Book.setBeanName invoke");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Book.destory invoke");
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke");
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("Book.setApplicationContext invoke");
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
System.out.println("setBookName: Book name has set.");
}
public void myPostConstruct(){
System.out.println("Book.myPostConstruct invoke");
}
// 自定义初始化方法
@PostConstruct
public void springPostConstruct(){
System.out.println("@PostConstruct");
}
public void myPreDestory(){
System.out.println("Book.myPreDestory invoke");
System.out.println("---------------destroy-----------------");
}
// 自定义销毁方法
@PreDestroy
public void springPreDestory(){
System.out.println("@PreDestory");
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("------inside finalize-----");
}
}
自定义实现BeanPostProcessor的MyBeanPostProcessor
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
// 容器加载的时候会加载一些其他的bean,会调用初始化前和初始化后方法
// 这次只关注book(bean)的生命周期
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean instanceof Book){
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean instanceof Book){
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
}
在resources目录下新建bean-liftcycle.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 扫描bean -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bean.lifecycle"/>
<!-- 实现了用户自定义初始化和销毁方法 -->
<bean id="book" class="com.bean.lifecycle.Book" init-method="myPostConstruct" destroy-method="myPreDestory">
<!-- 注入bean 属性名称 -->
<property name="bookName" value="thingking in java" />
</bean>
<!--引入自定义的BeanPostProcessor-->
<bean class="com.bean.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
做一个启动类的测试,新建SpringBeanLifecycleApplication
public class SpringBeanLifecycleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-lifecycle.xml");
Book book = (Book)context.getBean("book");
System.out.println("Book name = " + book.getBookName());
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy();
}
}
启动测试,输出结果如下
Book Initializing
setBookName: Book name has set.
Book.setBeanName invoke
Book.setBeanFactory invoke
Book.setApplicationContext invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
@PostConstruct
Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke
Book.myPostConstruct invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
Book name = thingking in java
@PreDestory
Book.destory invoke
Book.myPreDestory invoke
---------------destroy-----------------