HashMap
| HashMap | |
|---|---|
| 是否允许为空 | Key和Value都允许为空 |
| 是否允许重复数据 | Key重复会覆盖、Value允许重复 |
| 是否有序 | 无序,特别说明这个无序指的是遍历HashMap的时候,得到的元素的顺序基本不可能是put的顺序 |
| 是否线程安全 | 非线程安全 |
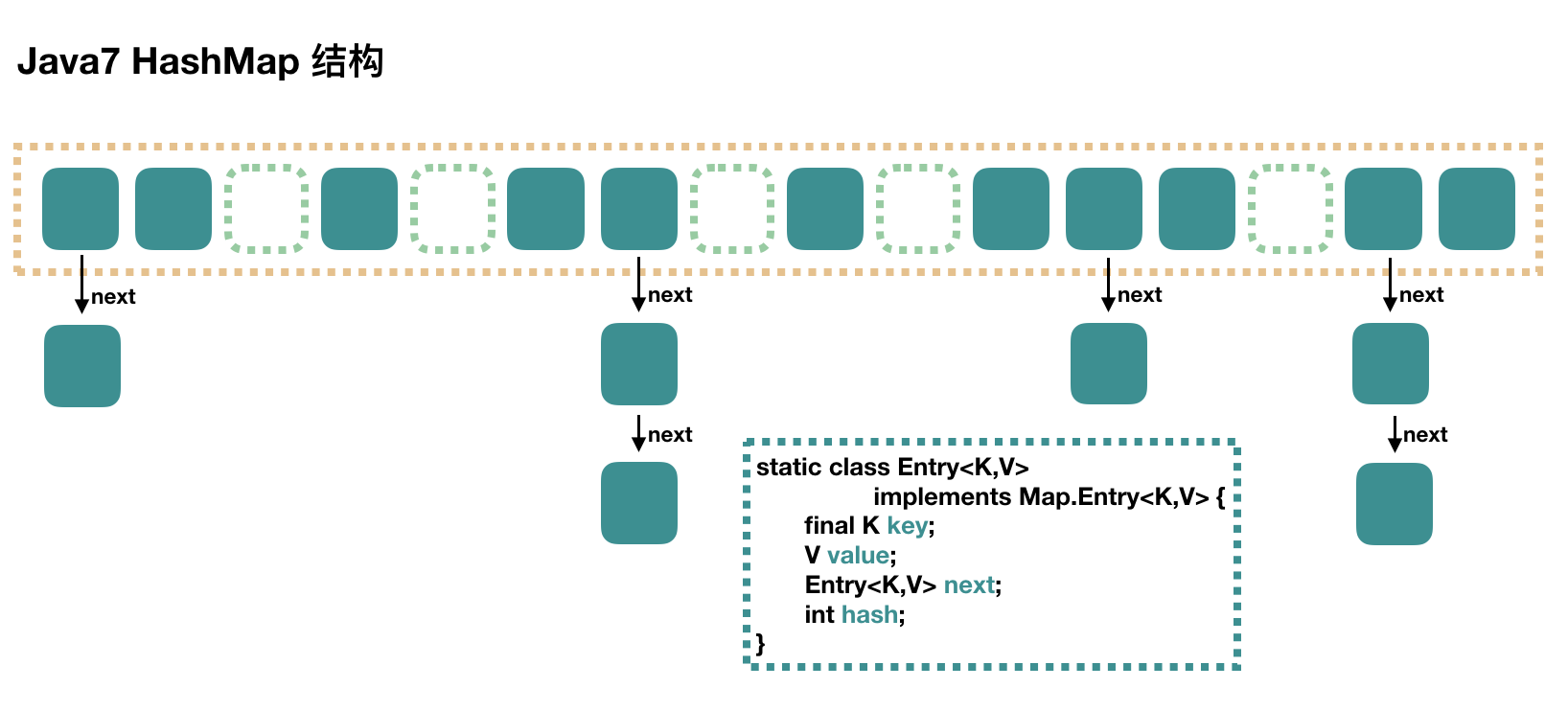
HashMap 里面是一个数组,然后数组中每个元素是一个单向链表。
上图中每个绿色方块是内部类Entry的实例,Entry有四个属性:key、value、hash和单向链指的next。
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
...
/**
* 默认初始化容量 - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* 最大容量, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
// 扩容的阈值 (capacity * load factor).
int threshold;
// 负载因子, 默认0.75
final float loadFactor;
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 当插入第一个元素的时候,需要先初始化数组大小
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 如果 key 为 null,感兴趣的可以往里看,最终会将这个 entry 放到 table[0] 中
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 1. 求 key 的 hash 值
int hash = hash(key);
// 2. 找到对应的数组下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 3. 遍历一下对应下标处的链表,看是否有重复的 key 已经存在,
// 如果有,直接覆盖,put 方法返回旧值就结束了
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 4. 不存在重复的 key,将此 entry 添加到链表中,细节后面说
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
// 在第一个元素插入HashMap时初始化数组, 并计算数组扩容的阈值
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// 保证数组大小一定是 2 的 n 次方。
// 比如这样初始化:new HashMap(20),那么处理成初始数组大小是 32
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
// 计算扩容阈值:capacity * loadFactor
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
// 算是初始化数组吧
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); //ignore
}
// 计算数组的位置
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
// 位移运算`&`效率比取模运算`%`高很多,主要原因是位运算直接对内存数据进行操作,不需要转成十进制,因此处理速度非常快
return h & (length-1);
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 如果当前 HashMap 大小已经达到了阈值,并且新值要插入的数组位置已经有元素了,那么要扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 扩容,后面会介绍一下
resize(2 * table.length);
// 扩容以后,重新计算 hash 值
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
// 重新计算扩容后的新的下标
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
// 将新值放到链表的表头,然后 size++
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
// 数组扩容
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 新的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 将原来数组中的值迁移到新的更大的数组中
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
// 由于是双倍扩容,迁移过程中,会将原来 table[i] 中的链表的所有节点,迁移到新的数组的 newTable[i] 和 newTable[i + oldLength] 位置上。
// 如原来数组长度是 16,那么扩容后,原来 table[0] 处的链表中的所有元素会被分配到新数组中 newTable[0] 和 newTable[16] 这两个位置。
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
// 步骤一 保留要转移指针的下一个节点
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
// 计算出要转移节点在hash桶中的位置
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
// 步骤二 使用头插法将需要转移的节点插入到hash桶中原有的单链表中
e.next = newTable[i];
// 步骤三 将hash桶的指针指向单链表的头节点
newTable[i] = e;
// 步骤四 转移下一个需要转移的节点
e = next;
}
}
}
public V get(Object key) {
// 之前说过,key 为 null 的话,会被放到 table[0],所以只要遍历下 table[0] 处的链表就可以了
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
//
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 确定数组下标,然后从头开始遍历链表,直到找到为止
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
...
}
...
}
假设在扩容过程中旧hash桶中有一个单链表,单链表中只有一个节点A,也就是e引用的对象。
新hash桶中有一个单链表,单链表中的节点是B->C,也就是newTable[i]引用的对象。
单线程下的扩容
- 执行到
步骤一时,next==null - 执行到
步骤二、三时,将节点A按头插法插入到newTable[i]所引用的链表中,此时newTable[i]单链表中的节点是A->B->C - 执行到
步骤四时,e=next,所以e==null,循环结束
多线程下的扩容
- T1线程执行到
步骤二时,会使得 e.next=newTable[i]=B - T2线程抢到CPU使用权执行到
步骤一时,会使得next不为空,next==B… - T1线程恢复CPU使用权继续执行到
步骤三时,将节点A按头插法插入到newTable[i]所引用的链表中,此时newTable[i]单链表中的节点是A->B->C - T1线程执行到
步骤四时,e=next,next=B,所以e==B,继续循环 - T1线程开启新的一轮循环执行到
步骤一时,next=e.next=C - 由于e==B,newTable[i]==
A,当T1线程执行到步骤二时,e.next=newTable[i]=A,将导致A.next==B, B.next==A…这时候如果用户发送一个get(A)的请求,将导致get请求发生死循环
- T1线程执行到
步骤二时,e.next=newTable[i]=A - T3线程执行
步骤一时,next==A,此时A.next==B, B.next==A, next==A,T1线程继续往下执行next指针会在A和B之间无线循环,导致T1扩容过程中发生死循环
为什么可以使用位运算 & 实现取模运算 % 呢?
h % 2^n = h & (2^n - 1)
2^n 表示2的n次方,也就是说,一个数对 2^n 取模等于一个数和 (2^n - 1) 做按位运算
假设 n = 3,则 2^3 = 8,二进制:1000,那么2^3 - 1 = 7,二进制:0111
此时 h & (2^3 - 1) 就相当于取 h 的二进制的最后三位数
从二进制的角度来看,h/8 相当于 h>>3 ,即把h右移3位,此时得到了 h/8 的商,而被移掉的部分(后三位),则是 h%8 ,也就是余数
如:
10 & 7 = 2
二进制位与运算:
001010
&
000111
=
000010
,